Why Disposable Medical Products are a must in Dental Care?
All the medical professionals are responsible for providing care to the patients who come to them seeking treatment for their sicknesses, ailments, and injuries. Patients entrust doctors and nurses with their health and healing, so it is vital that medical professionals stay vigilant in their efforts and be prepared for the diverse needs of their patients.
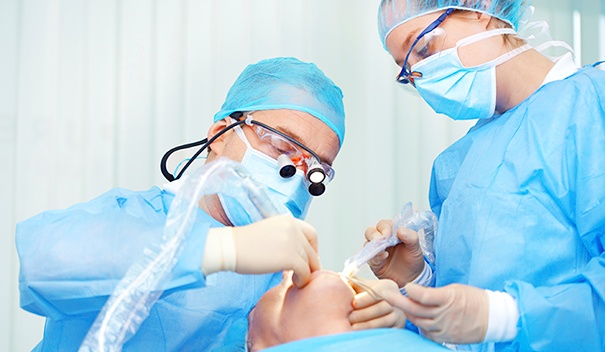
It is mandatory that dental health care workers wear gloves, surgical masks, protective eyewear, and protective clothing in specified circumstances to reduce the risk of exposures to bloodborne pathogens.
To properly prepare for the treatment of various injuries and wounds, medical professionals should make a habit of keeping wound care supplies adequately stocked and accessible, so they can treat their patients thoroughly and efficiently.
Transmission of Infections
Dental personnel may be exposed to a wide variety of microorganisms in the blood and saliva of patients they treat in the dental operatory. Infections may be transmitted in dental practice by blood or saliva through direct contact, droplets, or aerosols. Although not documented, indirect contact transmission of infection by contaminated instruments is possible. Patients and dental health-care workers (DHCWs) have the potential of transmitting infections to each other.
Re-usable and Single Use/Disposable Dental or Medical Products
Dental practice staff must be aware of the difference between reusable and single-use medical devices or items. If a medical device or item displays the single-use symbol on the packaging then it is deemed to be single use only or is a disposable medical product.
A single-use device is used on an individual patient during a single procedure and then discarded. It is not intended to be reprocessed and used again, even on the same patient.
Reuse of these devices can be unsafe because of the risk of:
- Cross-infection
- Inability to properly clean and decontaminate due to design.
- Endotoxin reaction
- Excessive bacterial breakdown products, which cannot be adequately removed by cleaning.
- Patient injury
- Device failure from reprocessing or reuse because of fatigue, material alteration and embrittlement.
- Chemical burns or sensitisation
- Residues from chemical decontamination agents on materials that can adsorb chemicals.
Examples of Single Use Devices
Single-use medical devices include, but are not restricted to the following:
- Endodontic reamers and files
- Saliva ejectors
- Aspirator tips and three-in-one tips
- Dental burs
- Matrix bands
- Single-use gloves
- Single-use face masks
Where instruments are difficult to clean considerations should be made to replacing them with single use items where possible.
Disposable or Single-use Medical Device Guidelines
There are a number of medical devices that are manufactured for limited reuse for the individual to whom they are initially supplied; ‘single patient use’ and for instruments that have a limited life; ‘limited use of instruments’. Staff who use or supply these devices to patients must understand all of the requirements for their safe use and disposal.
- It is the responsibility of the Dental Surgeon and Nurse to ensure that single-use devices are used only in the way directed by the instructions.
- It is the responsibility of the Dental Nurses to safely dispose of single-use devices immediately after use and not to reprocess such devices or to make them available for reuse.
- Re-useable medical devices should always be decontaminated in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.






Comments
Post a Comment